Effects of Heat: Increase in Temperature
Effects of Heat: Increase in Temperature: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Principle of Calorimetry, Heat Capacity and Rise in Temperature due to Heating.
Important Questions on Effects of Heat: Increase in Temperature
What is heat energy, and what are its effects?
Heat energy produces increase in temperature.
Define temperature.
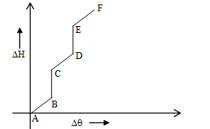
A solid is heated up and vs (Heat given, change in temperature) is plotted as shown in figure. Material exist in only one phase in-
When 100 mL of 1.0 M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insulated beaker at constant pressure, a temperature increase of was measured for the beaker and its contents (Expt.1). Because the enthalpy of neutralisation of a strong acid with a strong base is a constant , this experiment could be used to measure the calorimeter constant. In a second experiment (Expt. 2), 100 mL of 2.0 M acetic acid was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH (under identical conditions to Expt. 1) where a temperature rise of was measured.
(Consider heat capacity of all solutions as and density of all solutions as )
Enthalpy of dissociation of acetic acid obtained from the Expt. 2 is
Two spheres made of the same substance, have diameters in the ratio . Their thermal capacities are in the ratio of
If of heat is required to raise the temperature of moles of an ideal gas at constant pressure from to , then the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of same gas through same range at constant volume is
The specific heat capacity of a metal at low temperature () is given as A 100 g vessel of this metal is to be cooled from 20 K to 4 K by a special refrigerator operating at room temperature The amount of work required to cool the vessel is
Amount of heat required to convert 10 g of ice to water at 20 is
Water falls from a height of . What is the rise in temperature of water at the bottom if whole energy is used up in heating water?
If the ratio of densities of two substances is and that of the specific heats is . Then the ratio between heat capacities per unit volume is
Water of volume 2 L in a closed container is heated with a coil of 1 kW. While water is heated, the container loses energy at a rate of 160 J/s. In how much time will the temperature of water rise from 27oC to 77oC ? (Specific heat of water is 4.2 kJ/kg and that of the container is negligible).
The ratio of thermal capacities of two spheres and , if their diameters are in the ratio , densities in the ratio , and the specific heat in the ratio of, will be
Heat given to a body which raises its temperature by 1oC is